PROFESSIONAL EQUIPMENT,
INNOVATIVE TECHNOLOGY
The relative molecular mass of carbon dioxide is about 44, while the relative molecular mass of air is about 29. Because the specific gravity of carbon dioxide is larger than that of air, it is deposited on the surface of the earth, and it has the characteristics of heat absorption and heat insulation.
On the one hand, it absorbs a large amount of solar radiation, surface radiation, and other thermal radiation caused by human activities, resulting in an increase in temperature; On the other hand, it will block the surface radiation to a certain extent to dissipate heat outward, which is equivalent to forming a large cover of carbon dioxide in the air, and the thermal radiation can come in, but it is not easy to get out.

Some of the energy absorbed by land and ocean is also radiated into the atmosphere, and is also absorbed by greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide. Greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide efficiently absorb infrared radiation and scatter it in all directions. About 81% of the energy radiated from the Earth is captured by greenhouse gases and radiated back to the lower atmosphere close to the Earth, without returning to space. The dynamic heat exchange between the earth, the atmosphere and space is continuous, and a relatively stable thermal balance is established, so that the average temperature of the earth is well maintained, otherwise the earth may become very hot due to solar radiation, if the atmosphere does not reflect the heat of the earth's radiation back to the earth, the solar radiation received by the earth is all directly returned to space, and the earth will become cold.
However, if the concentration of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is too high, more than 81% of the solar radiation will return to the earth's surface, causing the earth's temperature to rise. Since the end of the 19th century, global carbon dioxide emissions have continued to increase, causing global temperatures to rise, causing a series of climate problems.
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is mainly caused by animal respiration, industrial and agricultural production, and other human activities, and plants and marine plankton can absorb a large amount of carbon dioxide and convert it into oxygen through photosynthesis, but there are few plants and dense crowds in the city, and it is easy to form a large amount of carbon dioxide accumulation. As a result, people often feel that the temperature in the city will be higher than in the suburbs and rural areas.

Greenhouse effect
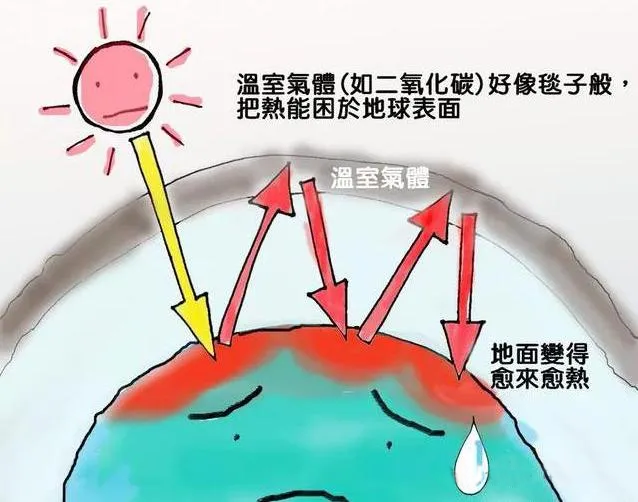
The greenhouse effect, also known as the flower house effect, is a common name for the atmospheric insulation effect. The atmosphere causes the solar short-wave radiation to reach the ground, but the long-wave thermal radiation emitted from the surface is absorbed by the atmosphere, which increases the temperature of the surface and the lower atmosphere, and is called the greenhouse effect because its effect is similar to that of a greenhouse for cultivating crops.
The greenhouse effect refers to the thermal insulation effect formed by the lack of heat exchange between the confined space that transmits sunlight and the outside world, that is, the solar short-wave radiation can penetrate the atmosphere into the ground, but the long-wave radiation released after the ground warms is absorbed by the carbon dioxide and other substances in the atmosphere, resulting in the effect of atmospheric warming.
The greenhouse effect is harmful
1. Global warming
Increasing concentrations of greenhouse gases reduce infrared radiation into space, which leads to warming of the Earth's surface and lower atmosphere. The United Nations agency predicts that by 2050, global carbon dioxide emissions will increase to 70 billion tons, and the global average temperature will rise by 1.5~4.5°C.
2. Sea level rise
High temperatures can cause icebergs to melt, and sea ice and polar ice caps are melting, increasing the amount of water in the oceans, which is causing sea levels to rise, and eventually many cities are under threat from sea level rise. Scientists predict that if the increase in the earth's surface temperature continues at the current rate, the global temperature will rise by 1.5~4.5 °C by 2050, resulting in a significant rise in sea level, and some island countries and coastal cities will be submerged, including several famous international cities such as New York, Shanghai, Tokyo and Sydney.
3. Diseases are rampant
The greenhouse effect has caused floods and droughts in high temperatures, creating an excellent environment for the virus to grow, and mosquitoes, ticks, rats and other disease-carrying organisms are becoming more and more abundant, resulting in frequent diseases. Globally, about 150,000 people die each year from diseases related to climate change. At the same time, respiratory problems caused by heat-related heart disease and malaria are also on the rise, as the warming environment increases the production of smog and increases the number of asthma attacks.
4. Deserts and floods
Global warming has reduced precipitation and surface runoff in the world's dry-stressed regions, exacerbated drought in these areas, and accelerated the rate of land desertification. On the other hand, climate warming will further increase the precipitation in tropical areas with heavy rainfall, thus exacerbating the occurrence of flood disasters.
5. Economic crisis
Climate change will lead to economic strains due to the effects of global warming, as huge amounts of capital must be spent to deal with natural disasters such as hurricanes and floods.

